|
The combustion parameters of gas mixturesAlthough there are examples of the direct utilization of pure waste gases in the industry it is better justified to use it as combination gas on account of the fluctuation in its heating value and its availability.
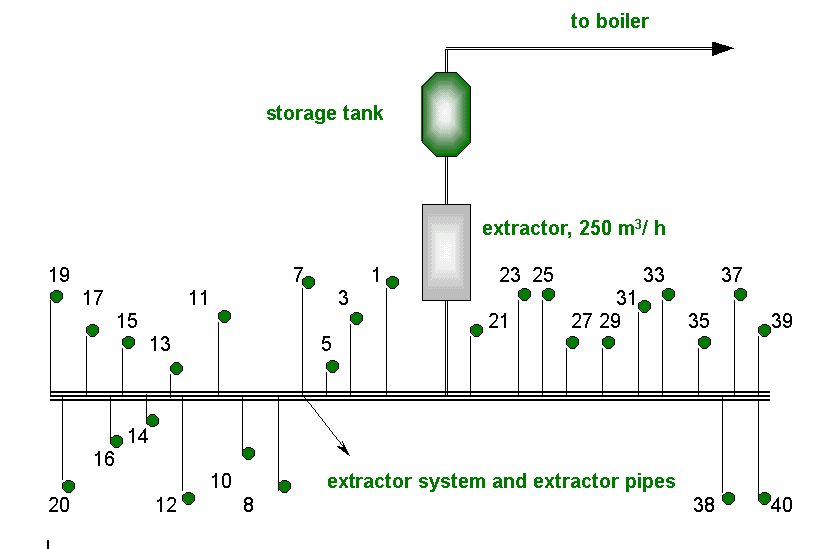
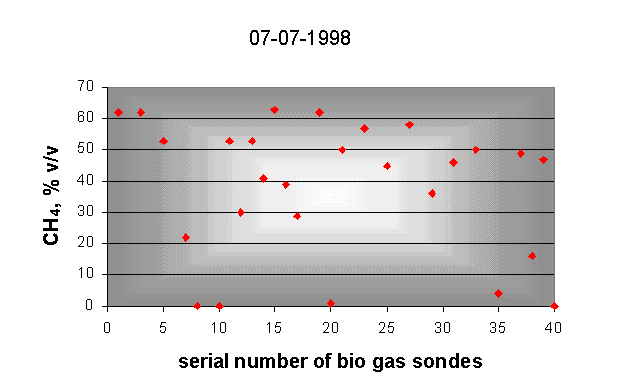
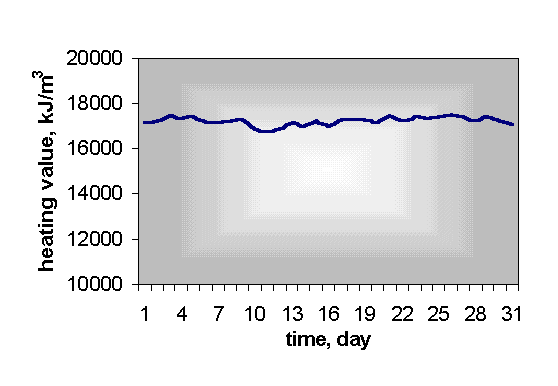
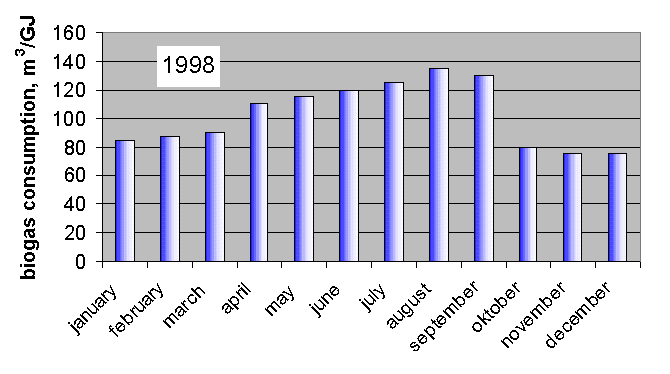
A bio gas collector can be seen in Fig. 1. and the change of
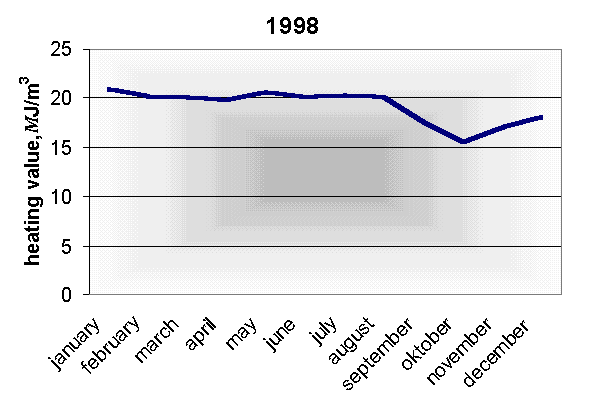
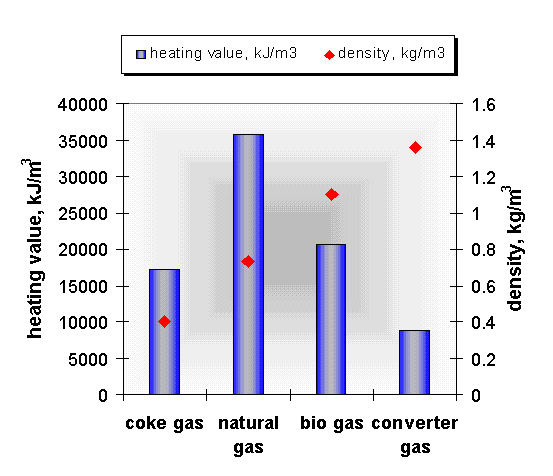
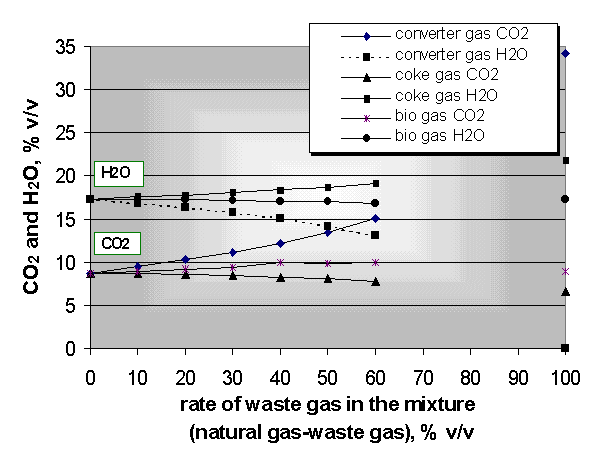
It is most suitable to mix it with natural gas because this increases and stabilises thermal value and equalizes fluctuation of bio gas quality (Fig. 5).
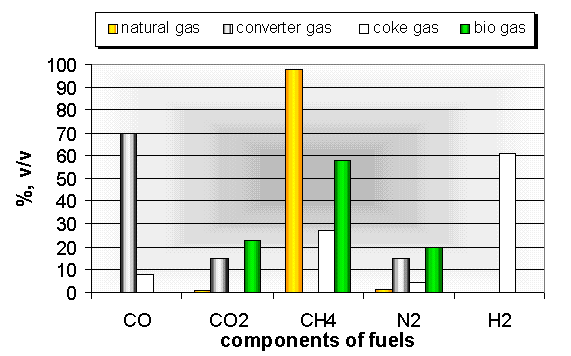
For our research project the basic calculations are done with a mixture of natural and waste gases. For the calculations natural and waste gases having the main composition indicated in Fig. 6 were used. The Fig. 7 gives the values of the main combustion parameters which are most important from point of view of burners. In our calculations the ratio of waste gases varied between 0 and 60% in the gas mixture, taking the practice into consideration.
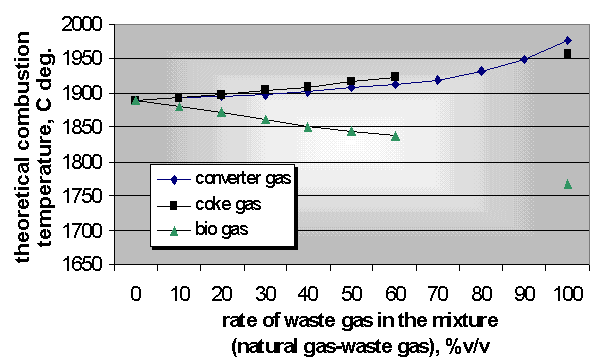
The same heat flow is guaranteed with increment of volume flow of fuel at different heating value of waste gases. For this reason the nozzle of burners applies transformation from time to time. The control of burners is necessary because of different density of waste gases . The theoretical combustion temperature plays a significant role in the heat technology and environmental protection. The bio gas has the minimum combustion temperature among the examined waste gases (Fig. 8) [3].
Mixing with natural gas rich in hydrogen the waste gases is favourable from the point of view
of radiational heat transfer which is primarily important for heating furnaces and boilers.
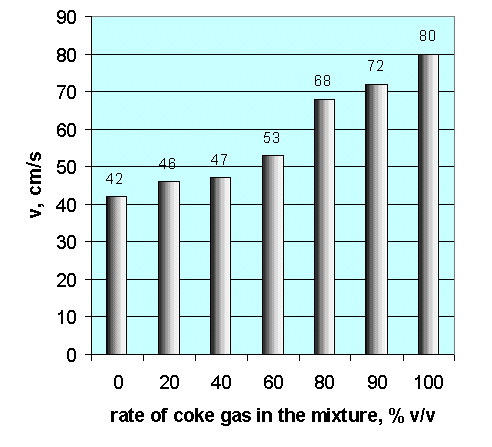
Coke gas increases the In the formation of the mixture of waste gas and natural gas it is important to know the rate of flame propagation as well as flammability limits. As it is not an additive parameter, therefore the normal rate of flame propagation of gas mixtures cannot be calculated from the composition with the help of the mixture laws. It can only be specified with the help of measurements [4]. Fig. 10 summarises the results of our measurements done to specify the exact values of flame propagation through example of coke gas [5].
|
|